Doctor-Blade vs Slot-Die: Choosing the Right Coating Method for Pharma-Grade ODFs
Share
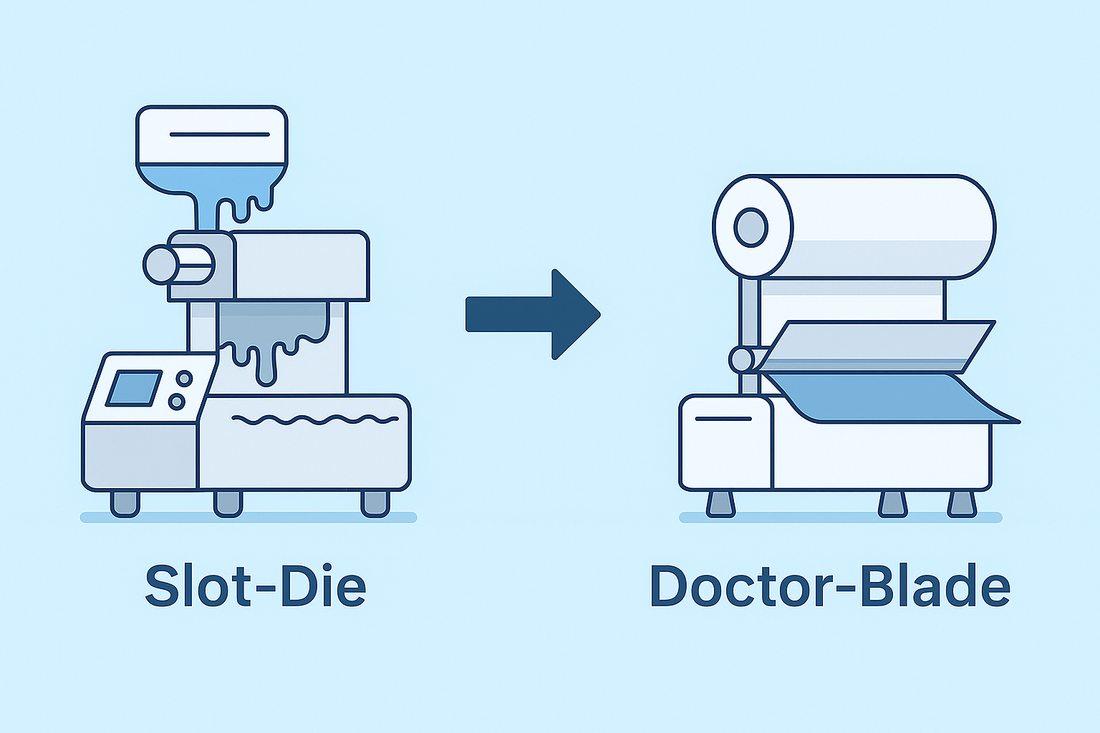
Summary: In ODF and transdermal patch manufacturing, the coating method largely determines film uniformity, process stability, and scalability. While slot-die excels in some web-coating industries, high-viscosity, multi-excipient pharma formulations often benefit more from a robust doctor-blade approach paired with controlled drying.
Introduction
For oral dissolvable films (ODFs) and solvent-based transdermal films, developers must manage variable rheology, solids content, and sensitive actives. Choosing between doctor-blade and slot-die isn’t interchangeable—each method has distinct requirements that affect coating quality, cleaning, and changeover. HUANGHAI systems adopt doctor-blade coating together with a natural hot-air gradient drying concept to deliver stable, GMP-ready performance.
Industry pain points with high-viscosity pharma coatings
- Rheology sensitivity: Slot-die requires tightly controlled viscosity and particle cleanliness; bubbles or fines can block the die and disrupt coating.
- Formulation complexity: Many ODFs use high-solids or multi-component matrices, causing flow instability and thickness bands.
- Cleaning burden: Intricate slot-die manifolds increase cleaning validation time and cost when recipes change frequently.
Why HUANGHAI chooses doctor-blade for ODF & transdermal films
- Wide formulation tolerance: Handles high-viscosity, high-solids slurries while maintaining uniform coat weight.
- Process simplicity & uptime: Open geometry reduces risk of “die-lines,” clogging, and lengthy disassembly.
- Micron-level control: Blade gap and line settings enable precise wet thickness targeting for consistent dry film.
- Energy-efficient drying: Natural hot-air gradient drying achieves the needed temperature profile without complex multi-zone control, supporting stable solvent removal and film morphology.
Principle comparison at a glance
| Aspect | Slot-Die | Doctor-Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Rheology tolerance | Narrow; susceptible to bubbles/solids | Broad; suitable for high-viscosity, multi-excipient slurries |
| Cleaning & changeover | Complex die internals; higher validation load | Simple blade/holder; fast, verifiable cleaning |
| Thickness control | Excellent in tightly controlled fluids | Micron-level via blade gap & line speed |
| Risk of defects | Die lines, streaks from partial blockage | Lower clogging risk; fewer flow-mark defects |
| Best fit | Low-viscosity, clean, stable webs | Pharma ODF/patch with variable, higher-viscosity matrices |
When slot-die may still make sense
If the formulation is low-viscosity, highly filtered, and the process runs at very tight rheology control with minimal recipe changeovers, slot-die can deliver excellent uniformity. For most pharma ODF and patch programs, however, doctor-blade offers a more forgiving, validation-friendly path.
Patent-backed approach
HUANGHAI’s doctor-blade plus gradient hot-air drying approach is protected under patent CN119869871A. See the disclosure on Google Patents: CN119869871A.
Compliance & scale-up value
- GMP suitability: Simplified hardware aids cleaning validation and documentation.
- Stable scale-up: Parameter windows (blade gap, speed, drying gradient) translate predictably from development to commercial lines.
- Lower lifecycle cost: Less downtime from die maintenance and fewer scrap events.
Recommended equipment
- MJ150-L ODF Coating Machine — pilot to medium-scale solution-casting and drying
- MJ150 ODF Coating Machine — commercial production capacity
Key takeaway
For pharma-grade ODFs and transdermal films, doctor-blade coating delivers the formulation tolerance, cleaning simplicity, and scale-up reliability that high-viscosity, multi-excipient systems demand—especially when paired with HUANGHAI’s natural hot-air gradient drying strategy.
